SPD Electrochromic Glass
-Switchable Dimmable and Durable
Structure of SPD Smart Glass:
SPD smart glass consists of multiple layers, including:
Two layers of glass or plastic.
A thin SPD film or layer in between, which contains suspended particles (usually microscopic rod-like particles) in a liquid or gel-like medium.
Conductive coatings (e.g., indium tin oxide) on the inner surfaces of the glass layers to apply an electric current.
Behavior of Suspended Particles:
Without Electricity (Off State):
When no voltage is applied, the suspended particles are randomly oriented.
These particles block and scatter light, making the glass appear dark or opaque.
With Electricity (On State):
When an electric current is applied, the particles align in a uniform direction.
This alignment allows light to pass through, making the glass transparent or clear.
Control Over Light and Transparency:
SPD smart glass can be adjusted to intermediate states between fully opaque and fully transparent by varying the voltage.
This allows for precise control over the amount of light and heat entering a space.
- Electrochromic spd film working principle
General features Standard film widths: 1200mm, 1500mm.
Standard formats: Rectangular sheets obtained by laser cutting, according to required dimensions.
Cutting and customisation: Possibility of cutting curved shapes, pre-cutting the strip for the electrodes, applying the electrodes to positions requested by the customer from a range of standard combinations.
Power supply: The BLUECHROMIC SPD switchable film is powered at 110Vac for the LIGHT GRADE version and 220Vac for the DARK GRADE / 50-60Hz version via transformer. Possibility of using our central dimmer.
Key Components of SPD Smart Glass:
Suspended Particle Film:
The core component that contains the light-blocking particles.
The particles are typically made of conductive materials that respond to electric fields.
Conductive Layers:
Transparent conductive coatings (e.g., indium tin oxide) are applied to the glass layers to create an electric field across the SPD film.
Power Supply:
An AC (alternating current) power supply is used to control the alignment of the particles.
The voltage required is typically low (e.g., 50–110V AC).
Control System:
SPD smart glass can be controlled via:
Manual switches.
Remote controls.
Smart home systems (e.g., Alexa, Google Home).
Automated systems (e.g., light sensors or timers).
Colours: LIGHT GRADE, DARK GRADE.
Total Transmittance (VLT)
Light Grade Switched off: ≤10% Switched on: ≥60%
Dark Grade Switched off: ≤1% Switched on: ≥35%
| Laminated Glass | ||||
| STATE | TVIS(%) | G-VALUE | REMARK | |
| Light Grade SPD (4 mm Clear+0,76EVA+SPD+0,76EVA+4 mm Clear) | OFF | 10 | 0.43 | MEASURED |
| 110V | 62 | 0.67 | ||
| Dark Grade SPD (4mm Clear+0.76EVA+SPD+0.76EVA+4mm Clear) | OFF | 2 | 0.39 | |
| 110V | 40 | 0.55 | ||
| 220V | 50 | 0.64 | ||
| Light Grade SPD + IR film (4mm Clear+0.38EVA+IR+0.38EVA+SPD+0.76EVA+4mm Clear) | OFF | 9 | 0.3 | SIMULATED |
| 110V | 51 | 0.45 | ||
| Light Grade SPD + Double Low-E coated glass (5mmSKN165+0.76EVA+SPD+0.76EVA+4mm Clear) | OFF | 8 | 0.21 | |
| 110V | 45 | 0.33 | ||
| Light Grade SPD + Double Low-E coated glass (5mmSKN154+0.76EVA+SPD+0.76EVA+4mm Clear) | OFF | 7 | 0.19 | |
| 110V | 36 | 0.29 | ||
SPD Elelctrochromic Glass Advanages
Good shading: it is in a light-transmitting state when on, and can absorb 99% of visible light when it is off.
One-button control: Transparency and darkness are converted into each other, and remote control is easy to control.
Fast transitions: state transitions within 1 to 5 seconds.
Two effects: blocking light and expanding the field of view .
The light changing by ourselves: People control the light.
Good thermal insulation: can block 99.9% of ultraviolet radiation, high thermal insulation performance.
Strong weather resistance: the operating temperature is -35C°~85C°, suitable for various climatic conditions.
Energy saving: reduce energy usage costs such as cooling costs, heating costs, lighting costs, etc.
Comfort Protection: Increase the comfort of the space and protect the internal items.
- SPD glass in dark state
- Electrochrimic smart glass power on state: total transparent
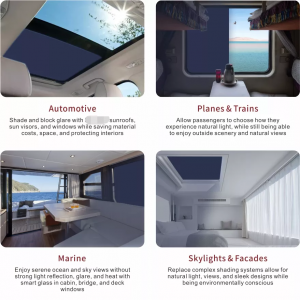
Popular Suitable application scenarios
Architectural Windows:
Used in skylights, facades, and partitions for dynamic light control.
Automotive:
Integrated into sunroofs, windows, and rearview mirrors for glare reduction and privacy.
Aviation:
Used in aircraft windows for adjustable shading.
Marine:
Installed in yacht windows and portholes for privacy and light control.
Healthcare:
Used in hospital windows and privacy screens.
Residential:
Ideal for smart homes, offering privacy and energy efficiency.
- Electrochromic smart glass suitable applications
How SPD Smart Glass Differs from Other Technologies:
Compared to PDLC (Polymer Dispersed Liquid Crystal):
PDLC glass becomes translucent in the opaque state, while SPD glass becomes dark or black.
SPD provides better control over light and heat, including UV and IR blocking.
PDLC requires continuous power to maintain transparency, while SPD does not.
Compared to Electrochromic Glass:
Electrochromic glass changes opacity through a chemical reaction and is slower to switch states.
SPD glass switches states faster and offers more precise control over light transmission.