Polymer Dispersed Liquid Crystal (PDLC) devices are a type of smart glazing or film that change their transparency in response to an electrical impulse.
1.Scattering PDLCs
The most common type of PDLCs are the optically scattering form. The concentration of polyer within the liquid crystal is roughly witin 30% ~50%. The polymer is cured with the Liquid crystals/Polymer emulsion,such as the droplets of liquid crystal seperate out within the polymer structure.
Liquid crystal molecules within each droplet have localised order, however each droplet can be randomly aligned relative to others. The combination of droplet size and isotropic orientation of droplets leads to a highly optically scattering state giving the cell a milky appearance. When the material is then subjected to an electric field, electro-optical reorientation of the liquid crystal droplets occures. This reduces the degree of optical scattering through the cell, giving rise to a transparennt state.
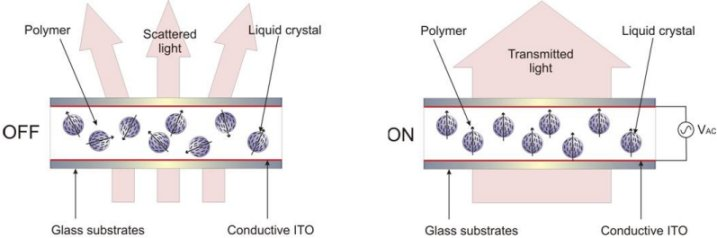
Scattering PDLCs are used as parivacy screens, windows (switchable between a transparent/clear state and an opaque/scattering state) and are commercially available. Chemical dye PDLC perferentially scattering red,green or blue light respectively. Many reasearchers are attempting to then use thse materils as RGB pixels in flexible displays.
2.Nano-PDLCs/Holographic PDLCs(H-PDLCs)
If the polymer concentration within a PDLC is increased to values of appromixmately 60%~80%, and then cured quickly(using high intensity UV ight sources), it is possible to form a PDLC with very small droplet size. Once droplet size reduces to approximately the nano size scale, tranmitted light through the mixture is no longer scattered at optical wavelengths.
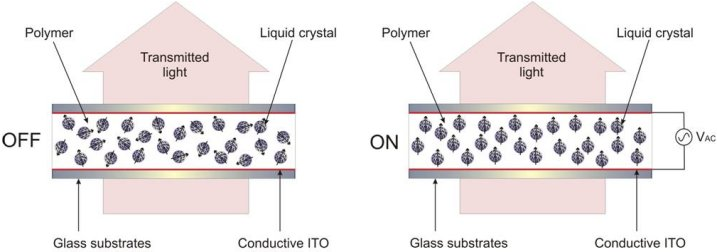
The resulting nano-PDLC mixture will still switch between randomly aligned and vertically aligned states when an electric field is applied, but no change in apparent scattering occurs. Instead, the optical phase of the transmitted light is modulated only, dermined by the average orientation ( and average refractive index) of the LC with the PDLC, Nano-PDLC phase-modulation devices have wide-ranging applications since they switch at every fast speeds(10s of microseconds), making them potentially suitable for wavefront correction devices in adaptive optics(used in astonomy, line-of-sight communications and ophthalmics).
Nano-PDLCs as ‘Holographic PDLCS’ (H-PDLCs) since they are often used for producing reconfigurable holograms.
3.Polymer stablised/Polymer network liquid crystals(PSLCs/PNLCs)
At the opposite extreme of polymer conentrations, in the region of approximately 1%~10%, the resulting PDLC mixture mostly consistency of a viscous liquid or gel. It’s electro-optical behaviour is almost identical to that of the LC on it’s own, but with improvements in switching times. Further imrpvements in switching times can also achieve via using sheared PNLCs.
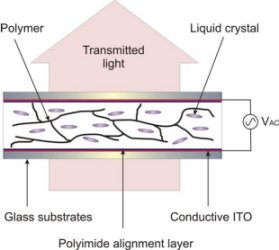
In this system, the cell is subjected to a shearing force, parallel to the glass substrates, which tends to orientate the polymer chains within the PNLC in the direction of the shearing movement. The resulting sheared PNLC devices have been quoted to have switching speeds of 10s of microseconds, comparable to those of nano-PDLCs but with far greater stroke and lower voltage requirements. Like conventional LC devices, PNLCs however are still polaration sensitive devices and require alignment layers to be deposited on the internal surfaces of the cell.